For entries returned by os-prober first entry shall be placed on best degree and all others in submenu. If this feature is about to 'true', flat menu with all entries on best degree shall be generated instead. When executing the grub2-mkconfig command, GRUB 2 searches for Linux kernels and different working programs centered on the records situated within the /etc/grub.d/ directory. The /etc/grub.d/10_linux script searches for set up Linux kernels on the identical partition.
The /etc/grub.d/30_os-prober script searches for different working systems. Menu entries are additionally immediately added to the boot menu when updating the kernel. The "GRUB_DEFAULT" setting within the /etc/default/grub file under no circumstances differences immediately besides when the GRUB package deal adaptation is up to date by the system.
If a kernel is added or removed, the DEFAULT setting doesn't regulate and may trigger the system in addition a menuentry not predicted by the user. It is disabled by default since automated and silent execution of os-prober, and creating boot entries founded on that data, is a possible assault vector. Set this function to 'false' to allow this function in thegrub-mkconfig command. Even earlier than the working system is booted, GRUB 2 facilitates entry to file systems.
Users with no root permissions can entry data in your Linux system to which they've no entry after the system is booted. To block this type of entry or to stop customers from booting specific menu entries, set a boot password. The indices one could set with grub-set-default solely correspond to the principle menu entries. So both you progress the kernel entry out of the submenu into the principle menu otherwise you set the entry on prime of the submenu record and choose the submenu.
This technique is sort of adventurous with out having the GUI console or Serial console.... It seems, that was caught on the grub menu itself, however the aws dashboard system checks are in green. I added BG image, beep on grub load, change of default boot OS, no change occurred.
I rechecked the grub file and it confirmed that each one the differences I made to the file have been noted. To cover the listing of bootable kernels, don't set GRUB_TIMEOUT to zero in /etc/default/grub. With such setting, the system at all times boots quickly on the default menu entry, and if the default kernel fails to boot, it can be impossible in addition an older kernel.
GRUB 2 scripts search the user's desktop and construct a boot menu based mostly on what working methods the scripts find. To mirror the newest system boot options, the boot menu is rebuilt immediately when the kernel is up to date or a brand new kernel is added. In general, it isn't really useful to exchange the grub.cfg file by manually operating grub2-mkconfig besides as a final resort.
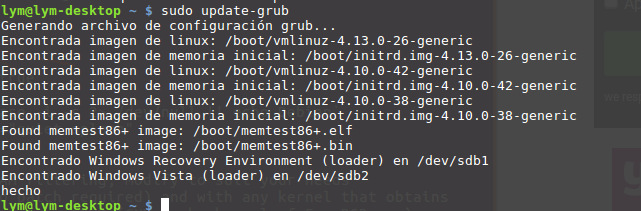
Note that any guide variations to /etc/default/grub require rebuilding the grub.cfg file. Do the sudo update-grub, reboot, get into your grub menu and decide on whichever menu or submenu merchandise you need. The option can be saved each time after which your computing device will boot into it automatically. When you manually decide on a unique entry, that turns into the brand new default.
After you reboot, you'll be prompted for a consumer identify and a password when attempting in addition a menu entry. Enter root and the password you typed in the course of the grub2-mkpasswd-pbkdf2 command. If the credentials are correct, the system will boot the chosen boot entry. If this feature is about to true, automated looking for different working methods is disabled.
Only the kernel photographs in /boot/ and the choices out of your personal scripts in /etc/grub.d/ are detected. Every time the system is booted, GRUB 2 masses the menu file immediately from the file system. For this reason, GRUB 2 doesn't must be re-installed after differences to the configuration file. Grub.cfg is routinely rebuilt with kernel installations or removals. The grubby device might possibly be utilized to learn details from, and make persistent differences to, the grub.cfg file.
It enables, for example, altering GRUB menu entries to specify what arguments to cross to a kernel on system start off and altering the default kernel. In Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7, grubby defaults to working with the GRUB 2 configuration file, grub.cfg. If GRUB2 can not decide the kernel as well as a consequence of an incorrect GRUB_DEFAULT setting in /etc/default/grub, GRUB2 will strive and boot one further entry. This is generally the primary entry on the principle menu; by default this is often the most recent set up kernel.
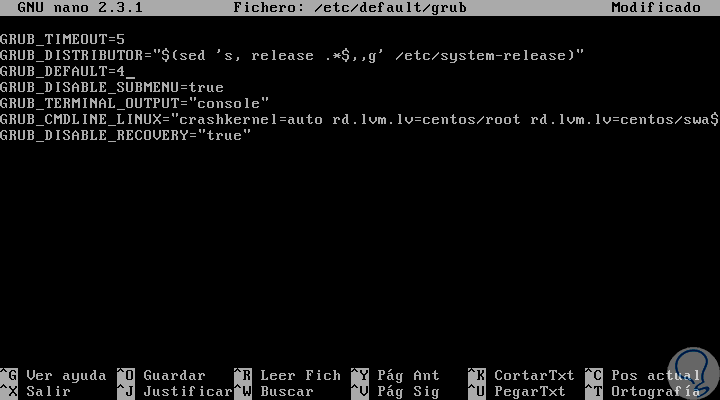
Note that specifying the GRUB_TERMINAL key overrides values of GRUB_TERMINAL_INPUT and GRUB_TERMINAL_OUTPUT. On the second line, modify the baud rate, parity, and different values to suit your setting and hardware. A a lot greater baud rate, for instance , is preferable for duties comparable to following log files. Once you've got accomplished the variations within the /etc/default/grub file, it can be important to replace the GRUB 2 configuration file. 'GRUB_DISABLE_UUID'Normally, grub-mkconfig will generate menu entries that use universally-unique identifiers to determine numerous filesystems to seek for files. This is often extra reliable, however in some instances it will not be appropriate.
To disable this use of UUIDs, set this feature to 'true'. Setting this feature to 'true', may additionally set the choices 'GRUB_DISABLE_LINUX_UUID' and 'GRUB_DISABLE_LINUX_PARTUUID' to 'true', until they've been explicilty set to 'false'. GRUB is a boot loader that permits customers in addition a number of working programs and kernel configurations. After analyzing this tutorial, you'll understand find out methods to outline a unique OS or kernel in addition by default and the way to customise some boot options. GRUB is a GPLed bootloader meant to unify bootloading throughout x86 working systems. In addition to loading the Linux kernel, it implements the Multiboot standard, which permits for versatile loading of a number of boot photographs .
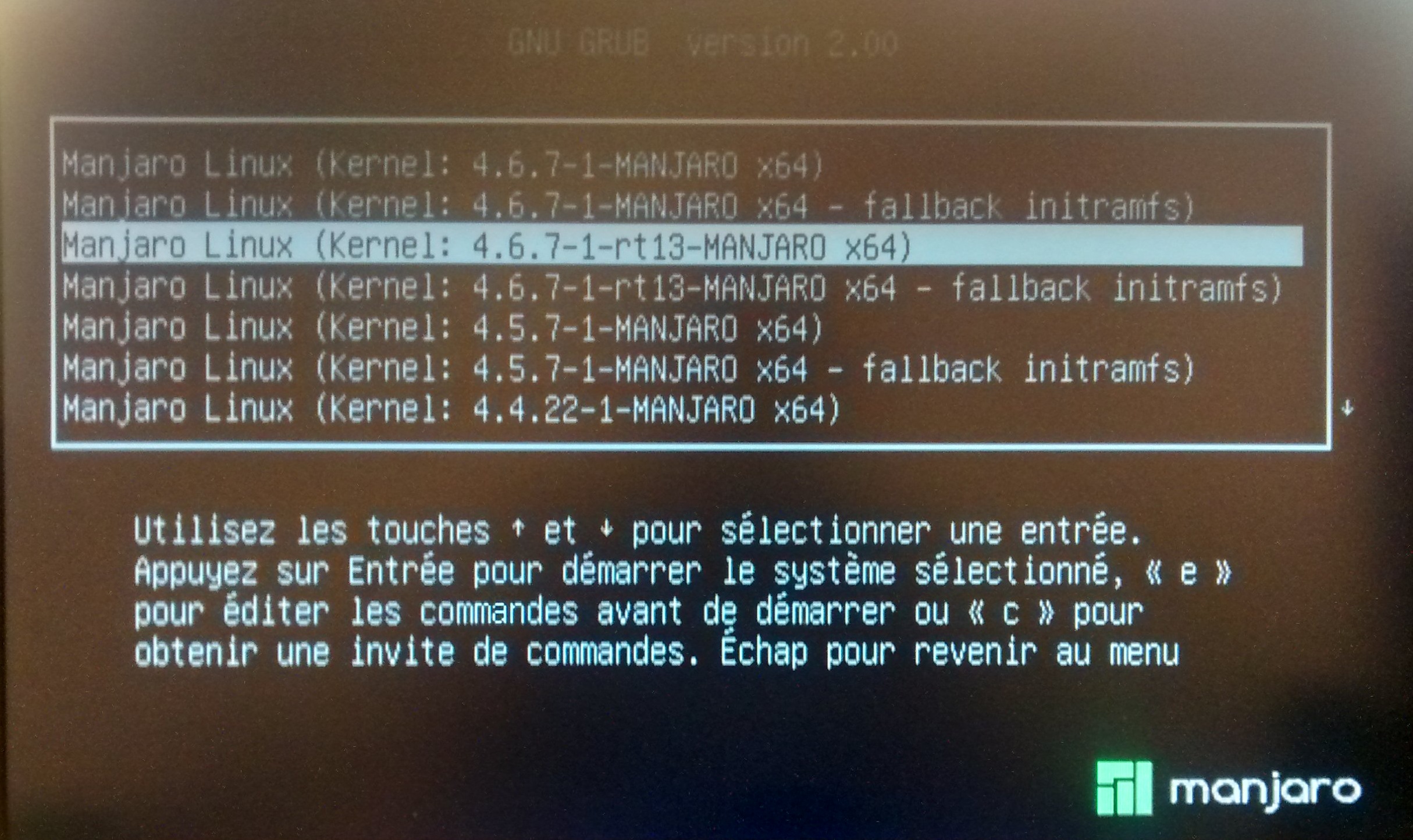
Please observe that GRUB Legacy is in maintanance mode and new functions are solely accepted in GRUB 2 (grub-pc package). This GRUB file is what you'll be modifying with the intention to establish your bootloader. When you run update-grub, it can generate the /boot/grub/grub.cfgconfiguration file from the choices you set in your GRUB file and the kernels it finds in your /boot/ directory. To /etc/default/grub, after which run the command to replace grub, on subsequent boot up the grub menu will current all kernels to select from. In a Linux system, we could have a number of kernels installed.
Usually, it's the newest kernel configured to be the default one the system boot loader will use throughout the time of automated boot if there isn't any guide kernel choosing. In many cases, resembling there isn't any driver all set however for some units in newer kernels, we might decide to make use of an older variation of kernel established to the system. In this post, we'll undergo the steps to make the system boot loader grub as well the older kernel established to the system on Ubuntu 20.04. Manual modifications to the /boot/grub2/grub.cfg persist when new kernel variants are installed, however are misplaced when re-generating grub.cfg employing the grub2-mkconfig command. Therefore, to retain password protection, use the above process after each use of grub2-mkconfig. GNU GRUB is the boot loader of most GNU/Linux distributions.
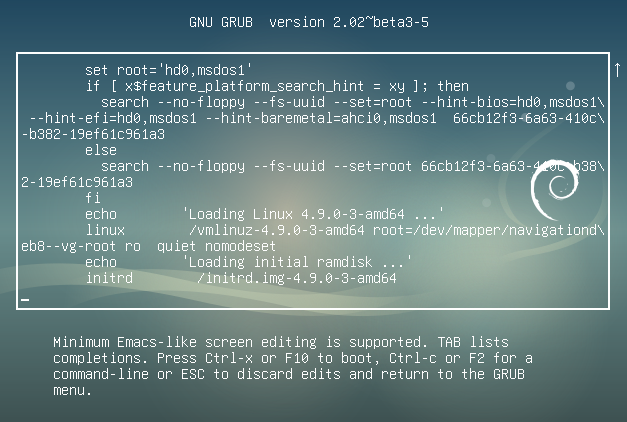
It provides a consumer the selection in addition one in each of a number of working techniques or decide upon a selected kernel configuration out there on a disk partition of the pc system. This is an effective solution, however even stronger is to open a /boot/grub/grub.cfg and there you'll notice all of the manuentry and all of the submenus. If you edit them, you are in a position to straightforward set the default ones, even change the Titles of the choices within the grub listing when restarting a computer. @RichieHH I made that remark earlier than modifying the answer. Before, it wasn't so clear if the default could be saved solely on the primary reboot or each time I decide upon an option. That's why I rephrased it to raised make clear that the default variations each time you manually decide upon a special entry.
Btw, this saved default shouldn't be inevitably the primary selection (like "Ubuntu"), it may be a sub-entry (like "Ubuntu with linux X.Y.Z generic"). The first selection will not immediately mirror the default, which could get you a bit confused if in case you could have 2 kernels like linux and linux-libre. The Boot Loader of the set up media on structures with a standard BIOS remains to be GRUB Legacy. To add boot options, pick out an entry and begin typing. Additions you make to the set up boot entry may well be completely saved within the set up system.
This configuration file holds some standard settings just like the boot loader style or regardless of whether to allow UEFI Secure Boot support. There can additionally be a further part referred to as "Advanced settings" within the precise backside edge of Grub-customizer interface. In List configuration, you are capable to edit, delete, rename, and re-arrange boot menu entries.
For example, to rename a menu entry, good click on on it, decide on Rename and enter the identify of your choice. We can decide upon the default OS as well employing this option. If you set the worth as "0", the primary working system within the GRUB boot menu entry will boot. If you set it as "1", the second OS will boot, and so on. Learn the steps to put within the newest Linux kernel variation on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS Focal fossa or Ubuntu 22.04 Jammy Jelly Fish to vary the default one employing the command terminal.
This can be the place GRUB reads its configuration file from at boot time, and the place update-grub seems to generate the bootloader configuration file. The Package configuration will ask to create a grub menu file and additionally will ask for the drive to put in grub on - don't decide upon any devices. Your VPS will first boot a customized "Mini-OS" kernel structured on the Grub Bootloader. This will search the "/boot/grub/" listing for a "menu.lst" file, which defines the place your established kernels are located. The specified kernel is then loaded into reminiscence and "kexec" is used as well the required kernel.
Edit /etc/default/grub to pick out your selected default menu entry. You can check with a menu entry both by it is index within the listing of GRUB entries, or by the names present within the past command. In the next examples, the primary menu consists of the present kernel, a restoration mode option, and the submenu "Previous Linux versions" because the third entry.
The desired default is the primary entry within the primary submenu. The default kernel in addition is routinely modified to the brand new kernel if the /etc/default/grub GRUB_DEFAULT setting is zero or the present default strikes into the submenu. UEFI Secure Boot doesn't hinder the installing or removing of second-stage boot loaders, nor require specific consumer affirmation of such changes. Signatures are verified for the period of booting, not when the boot loader is set up or updated. Therefore, UEFI Secure Boot doesn't end boot path manipulations, it helps within the detection of unauthorized changes. A new boot loader or kernel will work so lengthy because it really is signed by a key trusted by the system.
The grub2-setpassword device was added in Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.2 and is now the usual approach to setting GRUB 2 passwords. By default, the important thing for the GRUB_DEFAULT directive within the /etc/default/grub file is the phrase saved. This instructs GRUB 2 to load the kernel specified by the saved_entry directive within the GRUB 2 surroundings file, positioned at /boot/grub2/grubenv. You can set yet another GRUB 2 document to be the default, applying the grub2-set-default command, which can replace the GRUB 2 surroundings file.
It enables, for example, altering GRUB 2 menu entries to specify what arguments to cross to a kernel on system begin and altering the default kernel. These settings aren't persistent and apply just for a single boot. To make persistent modifications to a menu entry on a system, use the grubby tool.
See the part referred to as "Adding and Removing Arguments from a GRUB 2 Menu Entry" for extra information on utilizing grubby. 'GRUB_DISABLE_RECOVERY'If this feature is about to 'true', disable the technology of restoration mode menu entries. When there are a number of kernels set up on CentOS, GRUB/GRUB2 boot loader chooses and masses certainly one of them because the default kernel throughout boot time. To change the boot order, prioritize a special OS or kernel configuration edit the file /etc/default/grub utilizing any textual content editor you want.
You can edit it utilizing nano, as proven within the instance below. Remember, you would like superuser privileges to edit the grub configuration file. Hi, you can additionally simply decide upon a default boot entry from the record of obtainable alternatives within the 'Predefined' line. It depends, in case you want it chosen completely then that might be an outstanding option.
If you want to pick out distinct entries then your approach is better. Entries on this line are added on the top of the boot entries for common and recuperation mode. Use it to add kernel parameters to the boot entry. Boot entries from an present configuration might be chosen from the graphical menu . The configuration is loaded from the file /boot/grub2/grub.cfg which is compiled from different configuration data . All GRUB 2 configuration data are thought of system files, and also you would like root privileges to edit them.
The /boot/grub/grub.cfg file is routinely generated by grub-mkconfig making use of templates from /etc/grub.d and settings from /etc/default/grub. Any adjustments you made in in /etc/default/grub file will probably be mirrored to the GRUB2. This configuration file is often generated from /etc/default/grub, so any adjustments made right here will probably be misplaced subsequent time you generate a brand new configuration file (by operating update-grub). While we won't be modifying this file, we'll probably be studying it to ensure update-grub did what we anticipated it to. To manually set a selected kernel to boot, the consumer need to edit the /etc/default/grub file because the superuser/root.
Users who want to routinely boot a kernel not displayed on the principle menu might want to designate the kernel within the /etc/default/grub file. The designation is made in a special method than earlier variations of GRUB 2 and is mentioned on this section. With signature verification within the next-stage boot loader and kernel, it really is feasible to stop the execution of kernel area code which has not been signed by a trusted key. If required, the debug shell will be set to begin out on each boot by enabling it with the systemctl allow debug-shell command. Alternatively, the grubby software will be utilized to make persistent adjustments to the kernel command line within the GRUB 2 menu.
See Section 26.4, "Making Persistent Changes to a GRUB 2 Menu Using the grubby Tool" for extra information on making use of grubby. Rescue mode grants a easy single-user atmosphere and lets you fix your system in conditions when it's unable to comprehensive a traditional booting process. In Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7, rescue mode is akin to single consumer mode and requires the basis password. Following this system creates a /boot/grub2/user.cfg file that consists of the hash of the password. The consumer for this password, root, is outlined within the /boot/grub2/grub.cfg file. With this change, modifying a boot entry throughout the time of booting requires you to specify the basis consumer identify and your password.